How Does Price Floor Affect Equilibrium
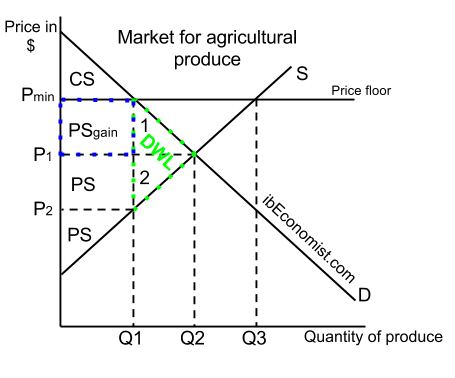
Price floors price floors are only an issue when they are set above the equilibrium price since they have no effect if they are set below market clearing price.
How does price floor affect equilibrium. A price ceiling is a type of price control usually government mandated that sets the maximum amount a seller can charge for a good or service. Price floor is enforced with an only intention of assisting producers. Suppliers can be worse off. This mutual adjustment continues until the price reaches p where producer and consumer decisions are perfectly coordinated.
If the price is below the equilibrium level the quantity demanded will exceed the quantity supplied so there will be a shortage. How does a price floor set above the equilibrium price affect quantity demanded and quantity supplied. A shortage means people want to buy more than firms are producing. A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
Consumers are always worse off as a result of a binding price floor because they must pay more for a lower quantity. Demanded and quantity supplied are equal. While they make staples affordable for consumers in. B it results in a greater quanatity supplied than the quantity demanded otherwise known as a exceess supply.
That will cause the price to rise. A it results in a smaller quantity supplied than the quantity demanded otherwise known as a shortage. As the price rises buyers will buy less and sellers will produce more. However price floor has some adverse effects on the market.
But if price floor is set above market equilibrium price immediate supply surplus can be observed. Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level. But the price floor p f blocks that communication between suppliers and consumers preventing them from responding to the surplus in a mutually appropriate way. When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded and excess supply or surpluses will result.
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded and excess supply or surpluses will result. When government laws regulate prices instead of letting market forces determine prices it is known as price control. When they are set above the market price then there is a possibility that there will be an excess supply or a surplus. The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the values of economic variables will not change often described as the point at which quanti.
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level. Price floors and price ceilings often lead to unintended consequences.