Floor Function Example In Oracle
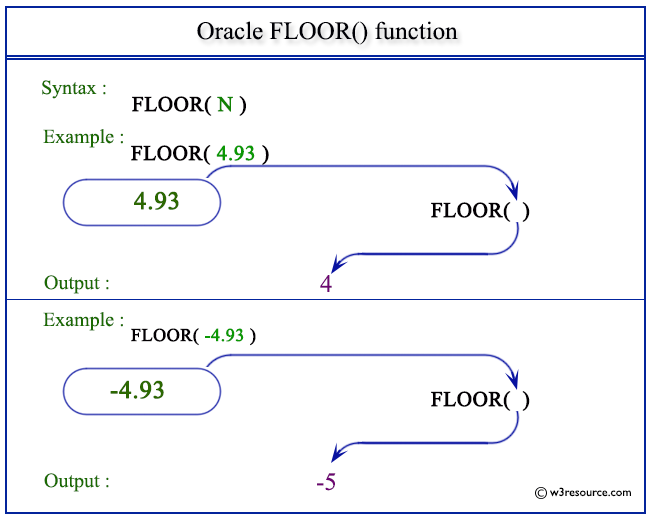
The statement below returns 4 which is the largest integer value of given number 4 93 as specified in the argument.
Floor function example in oracle. The oracle plsql floor function returns the largest integer value that is equal to or less than a number. This help is based on examples so it would be easier to understand. Floor and ceil unlike round and trunc do not take an optional parameter for precision because their output is always an integer. Oracle floor function allows to round a number down and the floor function removes all numbers after the decimal point.
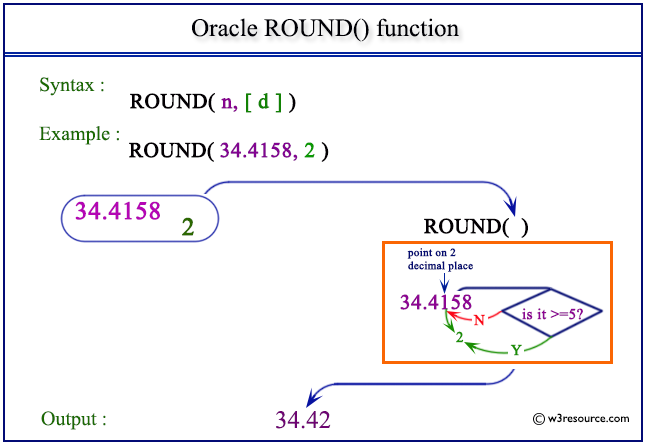
Example 1 rounded up. And this is the ceiling function. This example uses ceil and floor on a number that would normally be rounded up. Select floor 17 36 from dual.
Pictorial presentation of floor function. This oracle tutorial explains how to use the oracle plsql ceil function with syntax and examples. Description of the illustration floor gif purpose. Description of the illustration floor gif.
Floor returns largest integer equal to or less than n. Select ceil 41 8 as ceil test floor. Examples of the oracle ceil and floor function. The function returns the same datatype as the numeric datatype of the argument.
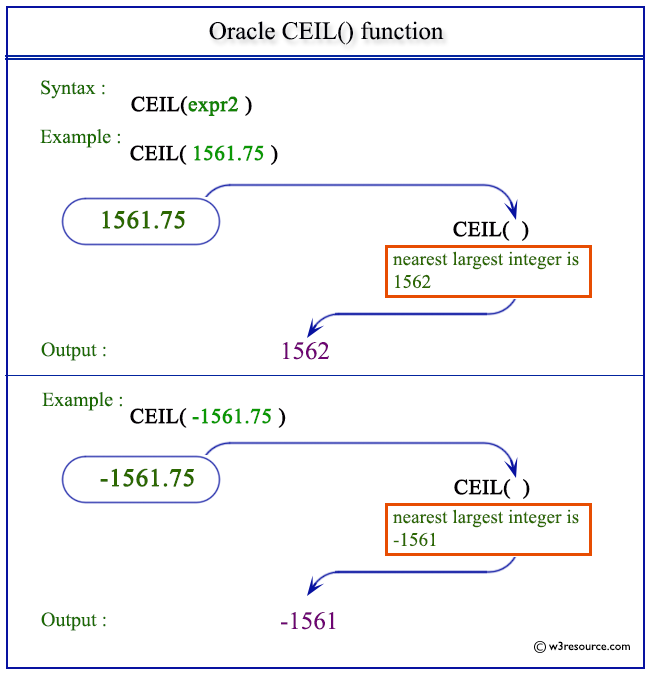
The oracle plsql ceil function returns the smallest integer value that is greater than or equal to a number. Mysql postgresql sql server and oracle. The syntax of oracle floor is. Some say int 3 65 4 the same as the floor function.
I find that examples are the best way for me to learn about code even with the explanation above. The following oracle floor example has input value 11 9999999 and function oracle round would have returned number 12 but since oracle floor rounds. This oracle tutorial explains how to use the oracle plsql floor function with syntax and examples. All of above platforms support the sql syntax of floor.
The floor function determines the largest integer less than or equal to a particular numeric value. This function takes as an argument any numeric datatype or any nonnumeric datatype that can be implicitly converted to a numeric datatype. Pictorial presentation of floor function. Conversely the ceil function determines the smallest integer greater than or equal to a particular numeric value.
Floor returns the largest integer equal to or less than n the number n can always be written as the sum of an integer k and a positive fraction f such that 0 f 1 and n k f the value of floor is the integer k thus the value of floor is n itself if and only if n is precisely an integer. Here are some examples of the ceil and floor functions.