Floor And Ceiling Functions Explained

Floor and ceiling in r is demonstrated with examples in this chapter.
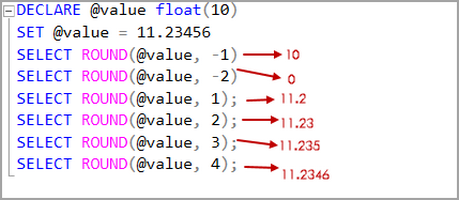
Floor and ceiling functions explained. Floor function takes the vector or column of the dataframe in r and rounds down those values. What is the floor and ceiling of 2 31. Definite integrals and sums involving the floor function are quite common in problems and applications. The ceiling function is usually denoted by ceil x or less commonly ceiling x in non apl computer languages that have a notation for this function.
Ceiling function takes the vector or column of the dataframe in r and rounds up those values. Int limits 0 infty lfloor x rfloor e x dx. The value of 21 on applying floor function is. Floor x function in r rounds to the nearest integer that s smaller than x.
Unlike roundup or rounddown excel s floor and ceiling functions can round the decimal places of a value to be divisible by a number you specify. With prices like 9 97 now in place of 9 99 and 9 47 in place of 9 49. For ceiling and. Math explained in easy language plus puzzles games quizzes worksheets and a forum.
Root is null return back to calling function. 0 x. The j programming language a follow on to apl that is designed to use standard keyboard symbols uses. 21 the value of 23 6 on applying floor function is.
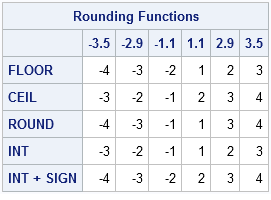
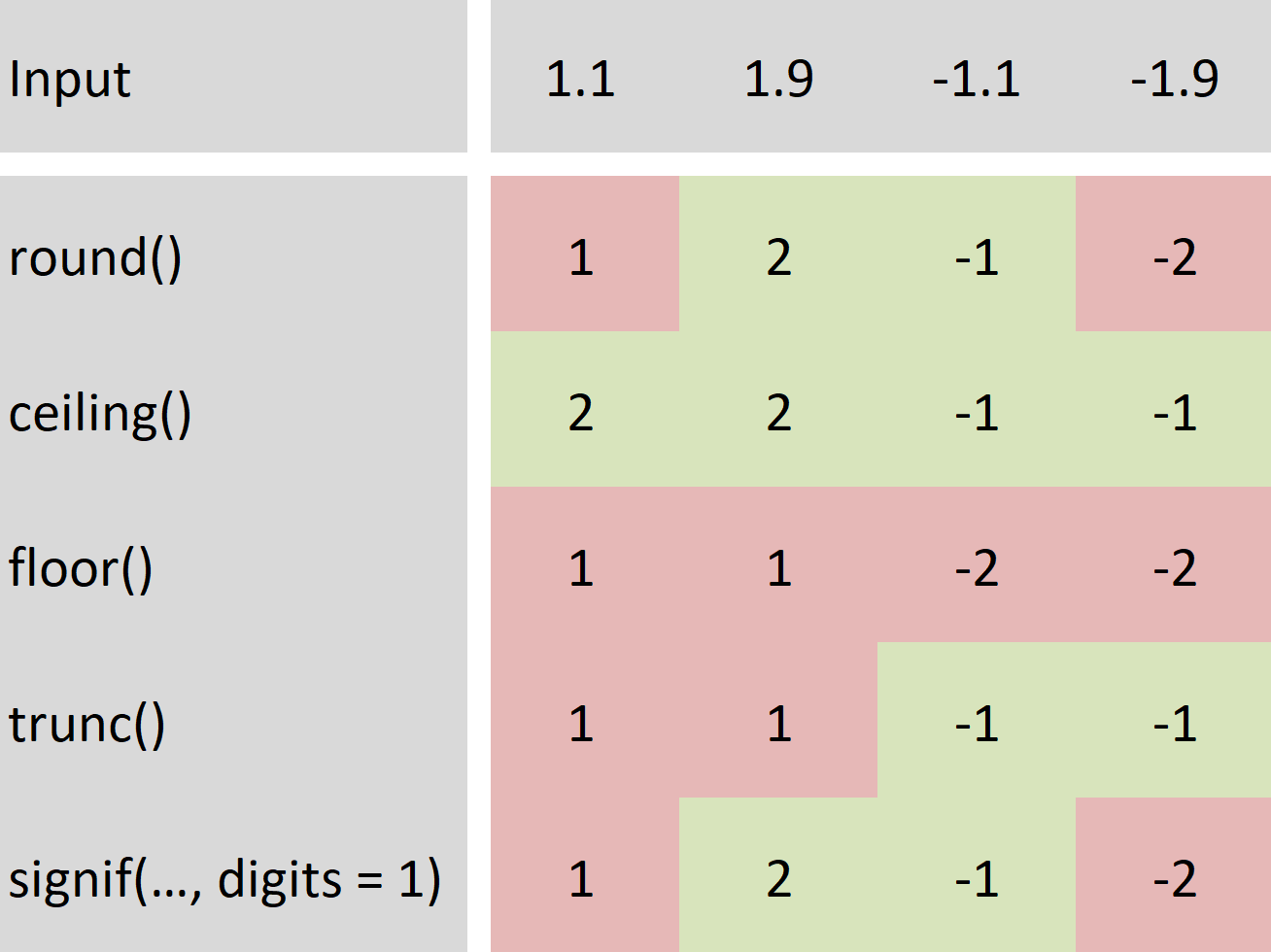
Hence we return back to calling function. The floor of 2 31 is 2 the. Floor and ceiling functions. The best strategy is to break up the interval of integration or summation into pieces on which the floor function is constant.
The floor and ceiling functions give us the nearest integer up or down. 14 ceil it accepts a number with decimal as parameter and returns the integer which is greater than the number itself. For k 12 kids teachers and parents. Veil x where x is a numeric value example of ceil.
Hide ads about ads. Evaluate 0 x e x d x. If tree is empty i e. A if current node data matches with the key value we have found both our floor and ceil value.